
It’s not easy to keep up with complex tax laws that always seem to be changing, much less figure out how they might affect you personally. Even so, it’s important to consider the potential impact of taxes when making many types of financial decisions.
The IRS automatically adjusts the standard deduction and income tax brackets annually for inflation. The rate of inflation rose to 40-year highs in 2022, so the 7% increases for 2023 are the largest since these adjustments began in 1985.1 The standard deduction is $13,850 for single filers in 2023 (up $900 from 2022) and $27,700 for married joint filers (up $1,800).
The filing deadline for 2023 federal income tax returns is April 15, 2024, (April 17 in Maine and Massachusetts, due to local holidays). Even though the 2024 tax year is well underway, there may still be time to take steps that lower your tax liability for 2023.
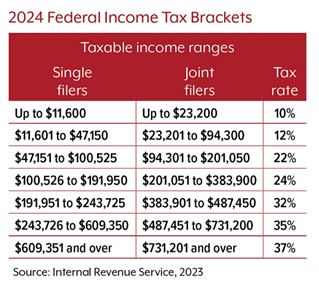
Understand “marginal” tax rates
U.S. tax rates increase at progressively higher income levels or brackets (see table). If your taxable income goes up and moves you into a higher bracket, the resulting tax increase might not be as bad as it may appear at first glance. For example, if you and your spouse are filing jointly for 2023 and have a taxable income of $110,000, you are in the 22% tax bracket. However, you will not pay a 22% rate on all of your income, only on the amount over $94,300.
Determining the value of certain deductions also depends on where your income falls in the tax brackets. Using the same example, a $10,000 deduction would reduce your income from $110,000 to $100,000 and theoretically reduce your tax liability by $2,200 (22% x $10,000). For a $20,000 deduction, you would have to calculate the amount of the deduction that falls in the 22% and 12% brackets: 22% x $15,700 + 12% x $4,300 ($3,454 + $516 = $3,970).
Although it’s helpful to know your marginal rate, your effective tax rate — the average rate at which your income is taxed (determined by dividing your total taxes by taxable income) — may offer a better way to gauge your tax liability.
Deduct large casualty losses
Wildfires, tornadoes, severe storms, flooding, landslides. The United States was struck by a record number of billion-dollar catastrophes in 2023.2 If something you own was damaged or destroyed by a disaster, and your loss exceeds 10% of your adjusted gross income (AGI) plus $100, you may be able to claim an itemized deduction on your federal income tax return. This typically applies to large losses that are uninsured or subject to a high deductible. For 2018 to 2025, a personal casualty loss is deductible only if it is attributable to a federally declared disaster.
The rules relating to casualty losses can be complicated. If you have suffered a significant loss, it may be worthwhile to consult a tax professional.
Apply for an extension
If you can’t meet the filing deadline for any reason, you can file for and obtain an automatic six-month extension using IRS Form 4868. (Otherwise, if you owe taxes, you might face a failure-to-file penalty.) You must file for an extension by the original due date for your return. For most individuals, that’s April 15, 2024; the deadline for extended returns is October 15, 2024.
An extension to file your tax return does not postpone payment of taxes. Estimate your tax liability and pay the amount you expect to owe by the original due date. Any taxes not paid on time will be subject to interest and possible penalties.
Pay yourself instead
Making deductible contributions for 2023 to a traditional IRA and/or an existing qualified health savings account (HSA) could lower your tax bill and pad your savings. If eligible, you can contribute to your accounts up to the April 15, 2024, tax deadline.
The 2023 IRA contribution limit is $6,500 ($7,000 in 2024). If you’re 50 or older, you can make an additional $1,000 catch-up contribution. If you or your spouse is covered by a retirement plan at work, eligibility to deduct contributions phases out at higher income levels.
If you were enrolled in an HSA-eligible health plan in 2023, you can contribute up to $3,850 for individual coverage or $7,750 for family coverage. (The limits for 2024 are $4,150 and $8,300, respectively.) Each eligible spouse who is 55 or older (but not enrolled in Medicare) can contribute an additional $1,000.
Avoid scams and costly mistakes
Tax season is prime time for identity thieves who may fraudulently file a tax return in your name and claim a refund — which could delay any refund owed to you. Or you might receive threatening phone calls or emails from scammers posing as the IRS and demanding payment. Remember that the IRS will never initiate contact with you by email to request personal or financial information, and will never call you about taxes owed without sending a bill in the mail. If you think you may owe taxes, contact the IRS directly at irs.gov.
The IRS has examined less than 0.5% of all individual returns in recent years, but the agency has stated plans to increase audits on high-income taxpayers and large businesses to help recover lost tax revenue. Wherever your income falls, you probably don’t want to call attention to your return.3 Double-check any calculations you do by hand. If you use tax software, scan the entries to make sure the math and other information are accurate. Be sure to enter all income, and use good judgment in taking deductions. Keep all necessary records.
Finally, if you have questions regarding your individual circumstances and/or are not comfortable preparing your own return, consider working with an experienced tax professional.
1) The Wall Street Journal, October 18, 2022
2) National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, 2024
3) Internal Revenue Service, 2024
IMPORTANT DISCLOSURES
The information presented here is not specific to any individual’s personal circumstances. To the extent that this material concerns tax matters, it is not intended or written to be used, and cannot be used, by a taxpayer for the purpose of avoiding penalties that may be imposed by law. Each taxpayer should seek independent advice from a tax professional based on his or her individual circumstances. These materials are provided for general information and educational purposes based upon publicly available information from sources believed to be reliable—we cannot assure the accuracy or completeness of these materials. The information in these materials may change at any time and without notice.
Securities and investment advice offered through Investment Planners, Inc. (Member FINRA/SIPC) and IPI Wealth Management, Inc., 226 W. Eldorado Street, Decatur, IL 62522. 217-425-6340.


